
Madagascar was one of the last major habitable landmasses on earth settled by humans. While there is some evidence of human presence on the island in the millennia B.C., large-scale settlement began between A.D. 350 and 550 with settlers from present-day Indonesia. The island attracted Arab and Persian traders as early as the 7th century, and migrants from Africa arrived around A.D. 1000. Madagascar was a pirate stronghold during the late 17th and early 18th centuries, and served as a slave trading center into the 19th century. From the 16th to the late 19th century, a native Merina Kingdom dominated much of Madagascar. The island was conquered by the French in 1896 who made it a colony; independence was regained in 1960.
During 1992-93, free presidential and National Assembly elections were held ending 17 years of single-party rule. In 1997, in the second presidential race, Didier RATSIRAKA, the leader during the 1970s and 1980s, returned to the presidency. The 2001 presidential election was contested between the followers of Didier RATSIRAKA and Marc RAVALOMANANA, nearly causing secession of half of the country. In 2002, the High Constitutional Court announced RAVALOMANANA the winner. RAVALOMANANA won a second term in 2006 but, following protests in 2009, handed over power to the military, which then conferred the presidency on the mayor of Antananarivo, Andry RAJOELINA, in what amounted to a coup d'etat. Following a lengthy mediation process led by the Southern African Development Community, Madagascar held UN-supported presidential and parliamentary elections in 2013. Former de facto finance minister Hery RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA won a runoff election in December 2013 and was inaugurated in January 2014. In January 2019, RAJOELINA was declared the winner of a runoff election against RAVALOMANANA; both RATSIRAKA and RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA also ran in the first round of the election, which took place in November 2018.
Visit the Definitions and Notes page to view a description of each topic.
Definitions and NotesSouthern Africa, island in the Indian Ocean, east of Mozambique
20 00 S, 47 00 E
total: 587,041 sq km
land: 581,540 sq km
water: 5,501 sq km
almost four times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Arizona
total: 0 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or 100 nm from the 2,500-m isobath
tropical along coast, temperate inland, arid in south
narrow coastal plain, high plateau and mountains in center
highest point: Maromokotro 2,876 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 615 m
graphite, chromite, coal, bauxite, rare earth elements, salt, quartz, tar sands, semiprecious stones, mica, fish, hydropower
agricultural land: 71.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 6% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 64.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 21.5% (2018 est.)
other: 7.4% (2018 est.)
10,860 sq km (2012)
most of population lives on the eastern half of the island; significant clustering is found in the central highlands and eastern coastline as shown in this population distribution map
periodic cyclones; drought; and locust infestation
volcanism: Madagascar's volcanoes have not erupted in historical times
world's fourth-largest island; strategic location along Mozambique Channel; despite Madagascar’s close proximity to the African continent, ocean currents isolate the island resulting in high rates of endemic plant and animal species; approximately 90% of the flora and fauna on the island are found nowhere else
27,534,354 (July 2021 est.)
noun: Malagasy (singular and plural)
adjective: Malagasy
Malayo-Indonesian (Merina and related Betsileo), Cotiers (mixed African, Malayo-Indonesian, and Arab ancestry - Betsimisaraka, Tsimihety, Antaisaka, Sakalava), French, Indian, Creole, Comoran
Malagasy (official) 99.9%, French (official) 23.6%, English 8.2%, other 0.6% (2018 est.)
note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Christian, indigenous, Muslim
Madagascar’s youthful population – just over 60% are under the age of 25 – and high total fertility rate of more than 4 children per women ensures that the Malagasy population will continue its rapid growth trajectory for the foreseeable future. The population is predominantly rural and poor; chronic malnutrition is prevalent, and large families are the norm. Many young Malagasy girls are withdrawn from school, marry early (often pressured to do so by their parents), and soon begin having children. Early childbearing, coupled with Madagascar’s widespread poverty and lack of access to skilled health care providers during delivery, increases the risk of death and serious health problems for young mothers and their babies.
Child marriage perpetuates gender inequality and is prevalent among the poor, the uneducated, and rural households – as of 2013, of Malagasy women aged 20 to 24, more than 40% were married and more than a third had given birth by the age of 18. Although the legal age for marriage is 18, parental consent is often given for earlier marriages or the law is flouted, especially in rural areas that make up nearly 65% of the country. Forms of arranged marriage whereby young girls are married to older men in exchange for oxen or money are traditional. If a union does not work out, a girl can be placed in another marriage, but the dowry paid to her family diminishes with each unsuccessful marriage.
Madagascar’s population consists of 18 main ethnic groups, all of whom speak the same Malagasy language. Most Malagasy are multi-ethnic, however, reflecting the island’s diversity of settlers and historical contacts (see Background). Madagascar’s legacy of hierarchical societies practicing domestic slavery (most notably the Merina Kingdom of the 16th to the 19th century) is evident today in persistent class tension, with some ethnic groups maintaining a caste system. Slave descendants are vulnerable to unequal access to education and jobs, despite Madagascar’s constitutional guarantee of free compulsory primary education and its being party to several international conventions on human rights. Historical distinctions also remain between central highlanders and coastal people.
0-14 years: 38.86% (male 5,278,838/female 5,196,036)
15-24 years: 20.06% (male 2,717,399/female 2,689,874)
25-54 years: 33.02% (male 4,443,147/female 4,456,691)
55-64 years: 4.6% (male 611,364/female 627,315)
65 years and over: 3.47% (male 425,122/female 509,951) (2020 est.)
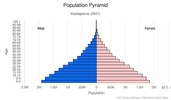
total dependency ratio: 75.9
youth dependency ratio: 70.5
elderly dependency ratio: 5.5
potential support ratio: 18.3 (2020 est.)
total: 20.3 years
male: 20.1 years
female: 20.5 years (2020 est.)
29.22 births/1,000 population (2021 est.)
6.09 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.)
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.)
most of population lives on the eastern half of the island; significant clustering is found in the central highlands and eastern coastline as shown in this population distribution map
urban population: 39.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.26% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
3.532 million ANTANANARIVO (capital) (2021)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.83 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2020 est.)
19.5 years (2008/09 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
335 deaths/100,000 live births (2017 est.)
total: 39.82 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 43.06 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 36.49 deaths/1,000 live births (2021 est.)
total population: 67.86 years
male: 66.54 years
female: 69.22 years (2021 est.)
3.7 children born/woman (2021 est.)
improved: urban: 87.9% of population
rural: 36.3% of population
total: 55.5% of population
unimproved: urban: 12.1% of population
rural: 63.7% of population
total: 44.5% of population (2017 est.)
0.18 physicians/1,000 population (2014)
0.2 beds/1,000 population
improved: urban: 42.5% of population
rural: 16.6% of population
total: 26.1% of population
unimproved: urban: 57.5% of population
rural: 83.4% of population
total: 73.9% of population (2017 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 76.7%
male: 78.4%
female: 75.1% (2018)
total: 10 years
male: 10 years
female: 10 years (2018)
total: 3.4%
male: 3.9%
female: 3% (2015 est.)
erosion and soil degredation results from deforestation and overgrazing; desertification; agricultural fires; surface water contaminated with raw sewage and other organic wastes; wildlife preservation (endangered species of flora and fauna unique to the island)
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
particulate matter emissions: 21.44 micrograms per cubic meter (2016 est.)
carbon dioxide emissions: 3.91 megatons (2016 est.)
methane emissions: 10.14 megatons (2020 est.)
tropical along coast, temperate inland, arid in south
agricultural land: 71.1% (2018 est.)
arable land: 6% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 64.1% (2018 est.)
forest: 21.5% (2018 est.)
other: 7.4% (2018 est.)
urban population: 39.2% of total population (2021)
rate of urbanization: 4.26% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
forest revenues: 4.34% of GDP (2018 est.)
coal revenues: 0% of GDP (2018 est.)
degree of risk: very high (2020)
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases: malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases: rabies
severe localized food insecurity: due to drought in southern areas and limited income-earning opportunities - an estimated 1.14 million people are food insecure in southern and southeastern regions and require urgent humanitarian assistance; the effects of a severe drought on agricultural production in 2021 and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly the loss of incomes due to the economic slowdown, are the key drivers of food insecurity (2021)
municipal solid waste generated annually: 3,768,759 tons (2016 est.)
municipal: 395 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
industrial: 161.9 million cubic meters (2017 est.)
agricultural: 13 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
337 billion cubic meters (2017 est.)
conventional long form: Republic of Madagascar
conventional short form: Madagascar
local long form: Republique de Madagascar/Repoblikan'i Madagasikara
local short form: Madagascar/Madagasikara
former: Malagasy Republic
etymology: the name "Madageiscar" was first used by the 13th-century Venetian explorer Marco POLO, as a corrupted transliteration of Mogadishu, the Somali port with which POLO confused the island
name: Antananarivo
geographic coordinates: 18 55 S, 47 31 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name, which means "City of the Thousand," was bestowed by 17th century King Adrianjakaking to honor the soldiers assigned to guard the city
6 provinces (faritany); Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina, Toliara
26 June 1960 (from France)
Independence Day, 26 June (1960)
history: previous 1992; latest passed by referendum 17 November 2010, promulgated 11 December 2010
amendments: proposed by the president of the republic in consultation with the cabinet or supported by a least two thirds of both the Senate and National Assembly membership; passage requires at least three-fourths approval of both the Senate and National Assembly and approval in a referendum; constitutional articles, including the form and powers of government, the sovereignty of the state, and the autonomy of Madagascar’s collectivities, cannot be amended
civil law system based on the old French civil code and customary law in matters of marriage, family, and obligation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Madagascar; in the case of a child born out of wedlock, the mother must be a citizen
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: unknown
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Andry RAJOELINA (since 21 January 2019)
head of government: Prime Minister Christian NTSAY (since 6 June 2018 and re-appointed 19 July 2019)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 November and 19 December 2018 (next to be held in 2023); prime minister nominated by the National Assembly, appointed by the president
election results: Andry RAJOELINA elected President in second round; percent of vote - Andry RAJOELINA (TGV) 55.7%, Marc RAVALOMANANA 44.3% (TIM)
description: bicameral Parliament consists of:
Senate or Antenimieran-Doholona (reestablished on 22 January 2016, following the December 2015 senatorial election) (63 seats; 42 members indirectly elected by an electoral college of municipal, communal, regional, and provincial leaders and 21 appointed by the president of the republic; members serve 5-year terms); note - in December 2020 Pres RAJOELINA ordered that the senate now have only 18 seats, 6 of which are appointed by the president, the remaining 12 indirectly elected by an electoral college of municipal, communal, regional, and provincial leaders; opposition parties' boycotted this legislative election
National Assembly or Antenimierampirenena (151 seats; 87 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 64 directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed-list proportional representation vote; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held 29 December 2015 (next to be held in 2021)
National Assembly - last held on 27 May 2019 (next to be held in 2024)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - HVM 34, TIM 3, MAPAR 2, LEADER-Fanilo 1, independent 2, appointed by the president 21; composition - men 51, women 12, percent of women 19%
National Assembly - percent of vote by party -Independent Pro-HVM 18%, MAPAR 17%, MAPAR pro-HVM 16%, VPM-MMM 10%, VERTS 3%, LEADER FANILO 3%, HIARAKA ISIKA 3%, GPS/ARD 7%, INDEPENDENT 9%, TAMBATRA 1%, TIM 13%; composition - men 120, women 31, percent of women 20.5%; note - total National Assembly percent of women 20.1%
highest courts: Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (consists of 11 members; addresses judicial administration issues only); High Constitutional Court or Haute Cour Constitutionnelle (consists of 9 members); note - the judiciary includes a High Court of Justice responsible for adjudicating crimes and misdemeanors by government officials, including the president
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court heads elected by the president and judiciary officials to serve 3-year, single renewable terms; High Constitutional Court members appointed - 3 each by the president, by both legislative bodies, and by the Council of Magistrates; members serve single, 7-year terms
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance
Economic liberalism and democratic action for national recovery or LEADER FANILO [Jean Max RAKOTOMAMONJY]
FOMBA [Ny Rado RAFALIMANANA]
Gideons fighting against poverty in Madagascar (Gedeona Miady amin'ny Fahantrana eto Madagascar) or GFFM [Andre Christian Dieu Donne MAILHOL]
Green party or VERTS (Antoko Maintso) [Alexandre GEORGET]
I Love Madagascar (Tiako I Madagasikara) or TIM [Marc RAVALOMANANA]
Malagasy aware (Malagasy Tonga Saina) or MTS [Roland RATSIRAKA]
Malagasy raising together (Malagasy Miara-Miainga) or MMM [Hajo ANDRIANAINARIVELO]
New Force for Madagascar (Hery Vaovao ho an'ny Madagasikara) or HVM [Hery Martial RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA Rakotoarimanana]
Total Refoundation of Madagascar (Refondation Totale de Madagascar) or RTM [Joseph Martin RANDRIAMAMPIONONA]
Vanguard for the renovation of Madagascar (Avant-Garde pour la renovation de Madagascar) or AREMA [Didier RATSIRAKA]
Young Malagasies Determined (Malagasy: Tanora malaGasy Vonona) or TGV [Andry RAJOELINA]and MAPAR [Andry RAJOELINA], and IRD (We are all with Andy Rajoelina) [Andry RAJOELINA]
ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, COMESA, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, InOC, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission:
Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Amielle Pelenne NIRINIAVISOA MARCEDA (since 31 October 2019)chancery: 2374 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 265-5525
FAX: [1] (202) 265-3034
email address and website:
contact@us-madagascar-embassy.org
consulate(s) general: New York
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Amy J. HYATT (since June 2021)
embassy: Lot 207A, Andranoro, Antehiroka, 105 Antananarivo
mailing address: 2040 Antananarivo Place, Washington DC 20521-2040
telephone: [261] 20-23-480-00
FAX: [261] 20-23-480-35
email address and website:
antanACS@state.gov
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and green with a vertical white band of the same width on hoist side; by tradition, red stands for sovereignty, green for hope, white for purity
traveller's palm, zebu; national colors: red, green, white
name: "Ry Tanindraza nay malala o" (Oh, Our Beloved Fatherland)
lyrics/music: Pasteur RAHAJASON/Norbert RAHARISOA
note: adopted 1959
Madagascar is a mostly unregulated economy with many untapped natural resources, but no capital markets, a weak judicial system, poorly enforced contracts, and rampant government corruption. The country faces challenges to improve education, healthcare, and the environment to boost long-term economic growth. Agriculture, including fishing and forestry, is a mainstay of the economy, accounting for more than one-fourth of GDP and employing roughly 80% of the population. Deforestation and erosion, aggravated by bushfires, slash-and-burn clearing techniques, and the use of firewood as the primary source of fuel, are serious concerns to the agriculture dependent economy.
After discarding socialist economic policies in the mid-1990s, Madagascar followed a World Bank- and IMF-led policy of privatization and liberalization until a 2009 coup d’état led many nations, including the United States, to suspend non-humanitarian aid until a democratically-elected president was inaugurated in 2014. The pre-coup strategy had placed the country on a slow and steady growth path from an extremely low starting point. Exports of apparel boomed after gaining duty-free access to the US market in 2000 under the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA); however, Madagascar's failure to comply with the requirements of the AGOA led to the termination of the country's duty-free access in January 2010, a sharp fall in textile production, a loss of more than 100,000 jobs, and a GDP drop of nearly 11%.
Madagascar regained AGOA access in January 2015 and ensuing growth has been slow and fragile. Madagascar produces around 80% of the world’s vanilla and its reliance on this commodity for most of its foreign exchange is a significant source of vulnerability. Economic reforms have been modest and the country’s financial sector remains weak, limiting the use of monetary policy to control inflation. An ongoing IMF program aims to strengthen financial and investment management capacity.
$41.82 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2020 est.)
$43.65 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2019 est.)
$41.81 billion note: data are in 2017 dollars (2018 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars